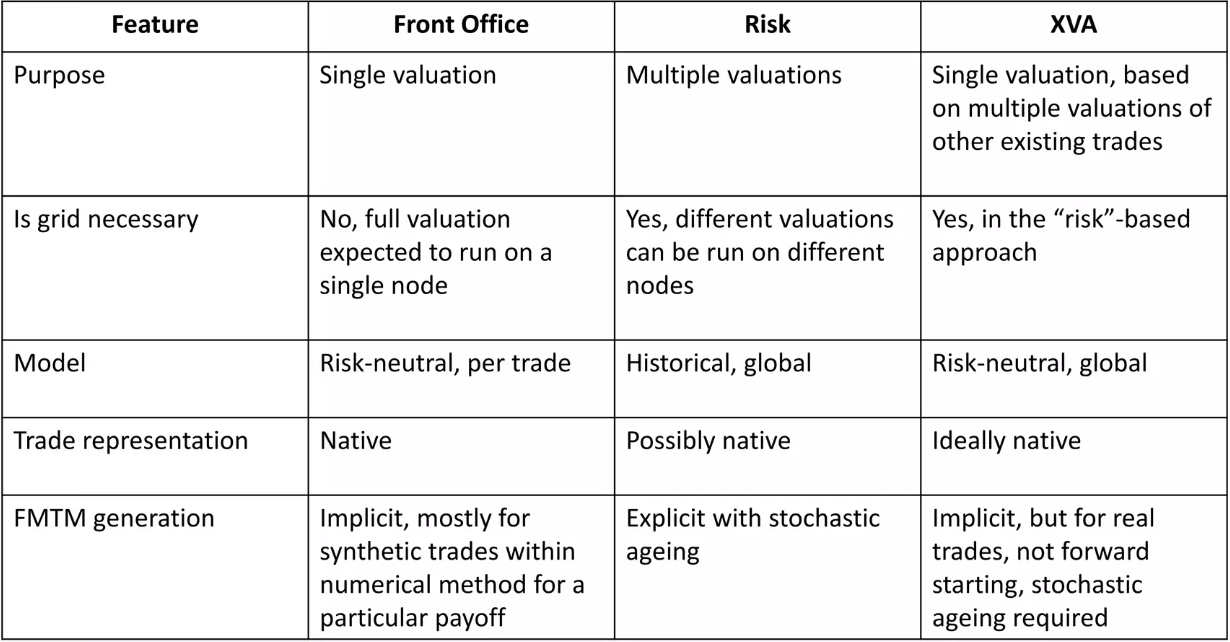
Summary:
With arrival of Basel III+ and the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book(FRTB), managing XVA has solidified its role as a front office operation. As a complex portfolio of credit default swaps, integrating XVA into a standard FO workflow can be challenging without significant trade compression. This complexity arise from several issues:
- Future MTMs (FMTMs) of trades in the netting set can exceed memory limits
- Overnight calculations may be too time consuming for complete risk an scenario analysis
- Collateral dynamics often match the intricacy of a securitisation waterfall.
One solution is to re-envision XVA as a hybrid derivative, allowing us to manage it by:
- Using FMTM generation as the final step in model calibration, and
- Treating collateral dynamics as a derivative pay-off for straightforward booking
This approach requires only minor adjustments to traditional front-office practices and clarifies the distinct roles of XVA quant teams versus other asset quant teams.
Key Competencies and tasks of the front-office QA and IT teams:
-
Trade booking which involves ensuring accurate and consistent trade representation across systems.This includes using templates or scripts, serialization for cross-system compatibility, compressing trades to manage large portfolios, and aging trades for accurate lifecycle representation
-
Market data: these teams handle everything from marking raw market observations to automatically marking simple derived values and pre-calibrating complex models, such as bond curves and volatility or correlation surfaces. This ensures a streamlined representation of market data.
-
Pricing: they generate future values of key market observables under the risk-neutral (RN) measure. Each product is priced through specific model calibrations and numerical methods, though this aspect is not directly used in hedging.
-
Greeks: which include advanced techniques like bump and recalculation and adjoint algorithmic differentiation (AAD) for efficient processing of deterministic scenarios. These combined tasks are essential for maintaining robust, real-time risk assessment and pricing capabilities in the front office.

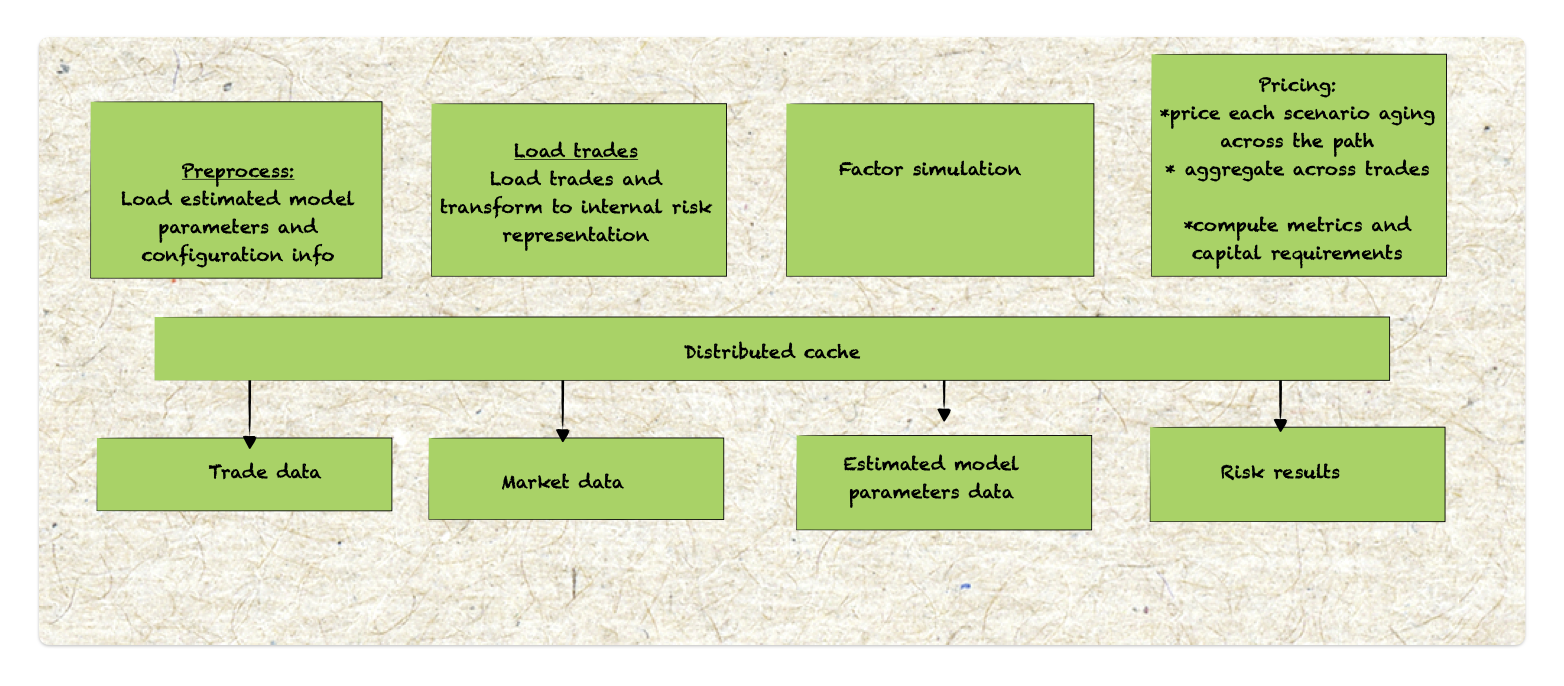
Key Competencies and tasks of the Risk QA and IT teams:
- Massive revaluation of trades using stochastic scenarios to assess risk across different market conditions. Their work often involves approximate pricing methods, using tools like front-office pricers, custom-built models, and sensitivity measures like delta, gamma, vega, volga, and vanna to efficiently capture market impacts.
- Generation of the market data scenarios under historical measure. They employ historical or parametric simulation for short-term market risk and Long term parametric simulation for CCR along with stochastic ageing of trades to capture extended scenarios.
- Develop baseline and stressed market data evolution model
- Calculation of distribution-driven risk measure, translating into economic and regulatory capital
- While they do not generate greeks for measures of PVs, they may rely on AAD if the PV function itself provides these values. This approach ensures efficient risk assessment that is aligned with regulatory demands while optimizing computational resources.
XVA as a CCDS ( of CFTD):
Way of looking at XVA as if it were a Contingent Credit Default Swap (CCDS) on a Contingent Forward Termination Date (CFTD). This approach essentially models XVA as an adjustable cost or protection instrument that reflects potential credit events and market shifts over a contingent period, providing a way to incorporate the costs of counterparty credit risk dynamically into the pricing and risk management of trades.
Key competencies:
- For XVA , Present Value(PV) is aggregated market value of the counterparty portfolio, which is the main calculation bottleneck( together with calibration.
- Initial Margin(IM) related XVAs may also require future greeks.
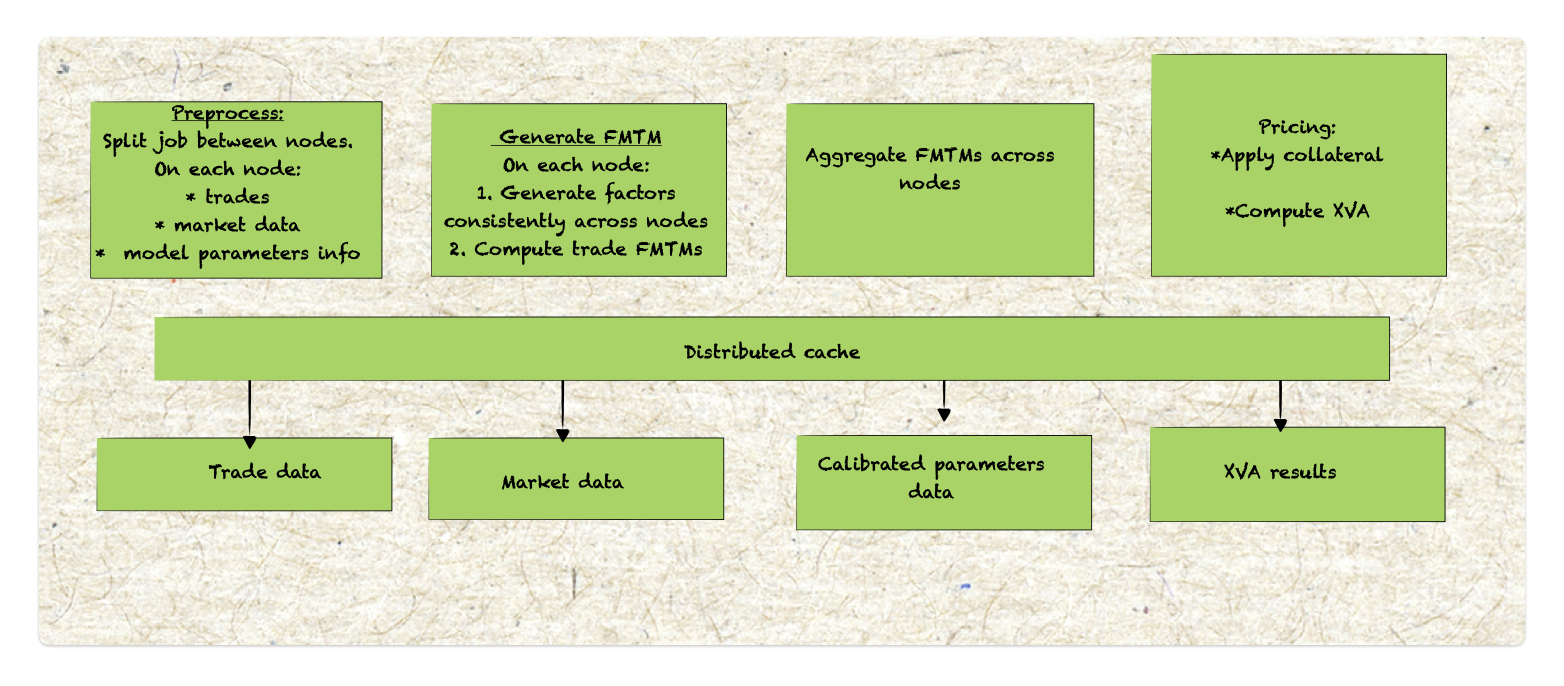
Why move to Front office?
Uncollateralized trades or trades with minimal collateral management require active XVA (valuation adjustment) hedging to address counterparty credit risks. To meet these regulatory demands, a per-counterparty, risk-neutral (RN) model is essential. This shifts XVA management into the front office domain, where sophisticated modeling and calibration practices are critical. A single, large hybrid risk-neutral model, though complex to calibrate, can effectively capture the interdependencies in these valuations.
To manage XVA risks under FRTB: Precise spot greeks of XVA are necessary, along with FMTMs need to be computed and possibly future greeks. Need much higher accuracy of numerical method to ensure XVA assessments are robust and aligned with FO standards. As a result BAU and pre-trade support expectations for XVA are increasingly in line with front-office practices, blending risk management with active, real-time valuation adjustments that fulfil both regulatory and market demands.