Margin serves as a risk mitigation tool and is calculated using several different techniques, depending on the regulatory framework and nature of the derivatives being traded.
ISDA SIMM(Standard Initial Margin model)
The ISDA SIMM calculates the potential future exposure (PFE) over a 10-day Margin Period of Risk (MPoR) at a 99% confidence level. This is achieved through a series of nested variance/covariance formulas, which are applied to aggregate results at different granular levels to derive the Initial Margin (IM).
-
Asset classes covered:
- Interest Rate (IR)
- Credit Risk (both qualifying and non-qualifying)
- Commodities (CM)
- Equities (EQ)
- Foreign Exchange (FX)
- Model Inputs:
- Trade sensitivities, which includes:
- Delta margin: Sensitivities of portfolio to market movements
- Vega margin: Sensitivities to changes in volatility
- Curvature margin: Non-linear sensitivities to price changes
- Trade sensitivities, which includes:
- Delta Margin calculation:
- Compute Sensitivities with respect to defined RF
- Apply risk weights
- Aggregate with prescribed correlation between the risk factors
- Algorithm process:
- Sensitivity grid computes individual risk position and aggregates them.
- Derivatives positions are classified into risk buckets.
- Risk factors are weighted based on their potential impact (MPoR weights)
- Aggregation is based on predefined buckets.
- SIMM satisfies BCBS(Basel committee of banking and supervision) guidelines
- SIMM parameters are calibrated using a 3-year look back + 1-year stress data
- Trade Data:
- Stored in XML format and loaded in ORE(Open source risk engine) to compute NPV and sensitivities.
-
CRIF File(Common Risk interchange Format): standard template to hold and report the risk data. Risk data format used to compute SIMM margin, SA-CVA , FRTB-SA amounts. ISDA recalibrate risk weights annually.
- SIMM features:
i) flexibility with collateral eligibility, but requires haircuts and does not allow for Wrong way risk(WWR).
ii) Transparent haircut calculation.
iii) Separation of asset classes
iv) SIMM parameters are calibrated using 3-year look-back period plus 1 stress year.
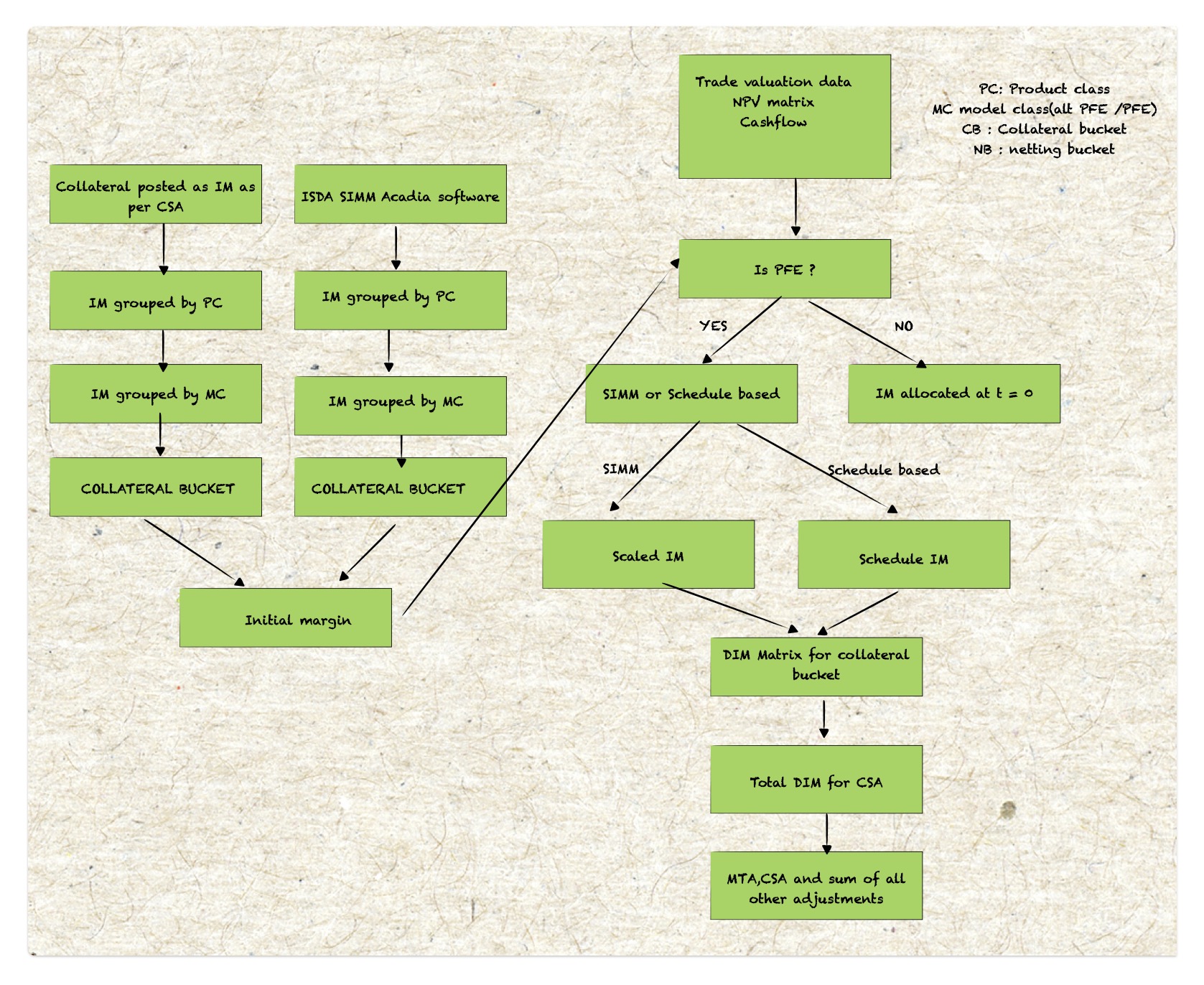
PFE Dynamic Initial Margin Model
Dynamic Initial Margin under uncleared margin rules relies on real-time valuation of derivative positions and is more computationally intensive than static models.
Dynamic IM Algorithm:
- Identify key Risk Factors e.g . Credit spread, Market vol, IR.
- Assess correlation among risk factors
- Collect real time market data for valuation
- Perform PFE simulations
- Calculate the Dynamic IM based on SIMM computations
- Calibration the Dynamic IM model
DIM model I/P:
a. Initial Margin from the SIMM model
b. Valuation matrices for both the base and shift scenarios
c. Simulated FX rates for non-USD cashflow/collateral conversions.
Upstream model: Uses PFE simulation data, including FX and ISDA SIMM results.
Downstream model: Aggregates PFE results and applies them to the Initial Margin calculations.
Collateral Buckets: Typically includes 1 CSA, 1 MC(model class), and 1 PC (Product class)
Scaled IM:
Non-path specific. IM is scaled with time and risk profile.
DIM(t) = min($DIM * min(R(t)/R(0) , 1)$
R(t)= $\sqrt{(Avg.(X^2(t,k))}$
X = netting set value change in portfolio from $t$ to $t+dt$, on path $k$.
Schedule-based IM:
At t = 0 Actual IM held.
Future value is % of notional based on time to maturity.
| Time to maturity | IM requirement as % of Notional |
|---|---|
| 0-2 | 2% |
| 2-5 | 5% |
| 5 > | 10% |
Rule based margin (Schedule based)
This is a simpler, rule-based approach where margin requirements are scheduled as a percentage of notional value, depending on time to maturity. It is less risk-sensitive but easier to implement than more sophisticated models like SIMM.
IMM(internal model method)
The Internal model method is used to calculate capital requirements according to Basel III. This method allows banks to use internal models to determine risk and margin. But it requires regulatory approval, which involves a rigorous assessment of the model’s accuracy, robustness and compliance with standards.