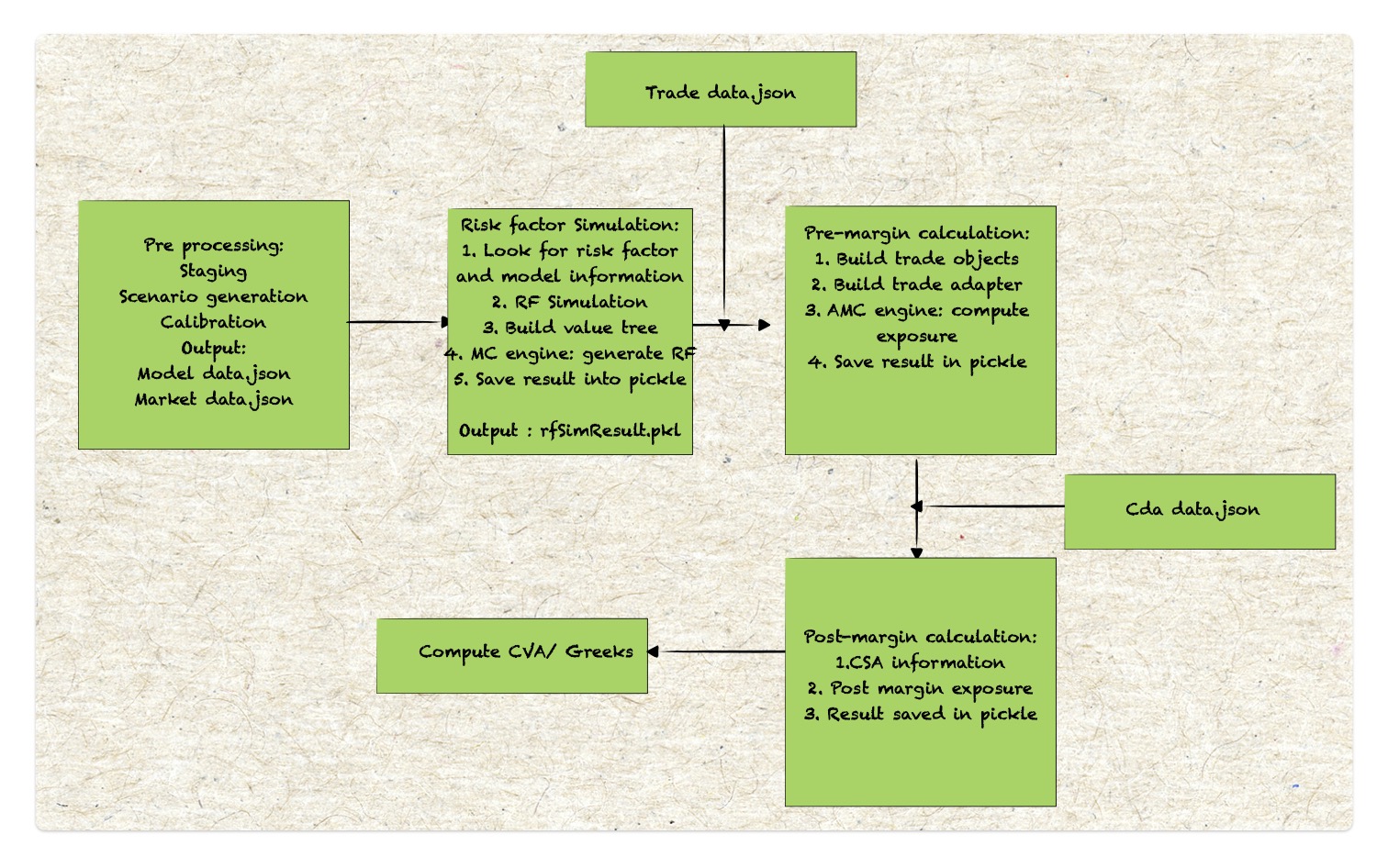
The cross-asset XVA framework consists of four primary modules plus one random number generation. The key modules are:
- Market generation/simulation
- Trade Valuation
- Aggregation
- XVA computation
XVA random number generation: The random number generator produces correlated random normal shocks, using a correlation matrix of risk factors estimated from historical data. These shocks are used to simulate the evolution of the risk factors.
Simulation: A global grid is applied for the portfolio and time-step construction. This grid determines the credit dates used in the simulation. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of results, convergence tests are performed for the grid parameters, along with stability tests for different CSA(Credit support annex) parameters.
Trade valuation: There are several methods to determine trade values in XVA framework:
- Front Office(FO) Pricers: Call the trading desk pricers to get the mark-to-market(MtM) values directly.
- FO pricers with Adjustments: Use FO pricers, factoring in settlements, resets, and other trade details.
- Tree-Based calculations: For certain products like single-currency interest rate swaps(IRS), a trinomial tree is used to calculate values, and linear interpolation is applied to estimate values on each Monte Carlo(MC) simulation path.
- Regression Techniques: Longstaff-Schwarz least square regression. e.g for FX products
For commodity valuation, to improve speed, a sub-sample of the simulation paths is priced with desk models. For the remaining paths, trades values are approximated as linear interpolation based on market data and well defined independent variables.
Aggregation:
Aggregation involves integrating CSA parameters such as netting, collateral, default windows, and margin period of risk. This process outputs both collateral and exposure values.
Net Present Value(NPV) matrix are calculated for each counterparty. These matrices are then combined, cell-by-cell, to generate a single matrix that represents the netted NPVs for each simulation path and time point. A counterparty may have multiple netting groups, and each netting group can have multiple collateral groups.
XVA valuation: For XVA computation, the probability of Default (PD) and loss given default (LGD) can be derived either from market-implied data or model-based methods. PD is typically determined using a “waterfall” approach, which considers characteristics like CDS spreads, traded bonds, and loans.
OIS Discounting in XVA computation : OIS(Overnight Index Swap) rates are used for discounting, not because they are risk-free, but because they reflect the rate it which margins are remunerated (held daily). The increasing divergence between LIBOR/BBSW and OIS has made OIS the preferred choice for discounting.
Adjustment Interactions:
When a counterparty defaults, Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) comes into play. However, throughout the lifecycle of a transaction, additional adjustments such as Funding Valuation Adjustment (FVA), Collateral Valuation Adjustment(ColVA), Capital Valuation Adjustment(KVA), and Margin Valuation Adjustment(MVA) are necessary. There is significant interaction between these adjustments, and teams need to collaborate closely to avoid double counting.